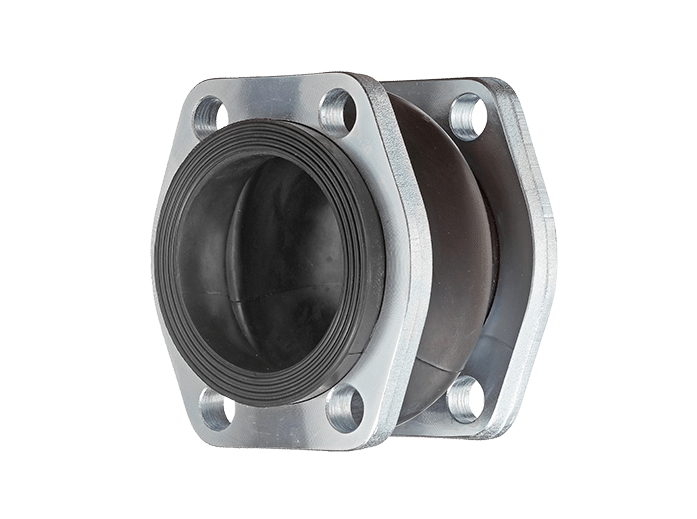
Hydraulic Rubber Compensators
Hydraulic rubber compensators dampen vibrations and noise, as well as protect your pipes from axial and radial stress. Designed for low-pressure suction lines. Sizes from 25-100 mm (1-4 in) handling pressures of up to 116 psi (8 bar).

Need Support? We Can Help.
What Makes Us Different?

Fast lead times
Popular SAE flanged models in stock. Non-stock models are fulfilled within 6-8 weeks, or less with expediting available.

Limited market speciality
These designs are limited within the market. We are one of the few trusted suppliers.

On-demand experts
Our team stays responsive to your specifications and inquiries while ensuring fast lead times.
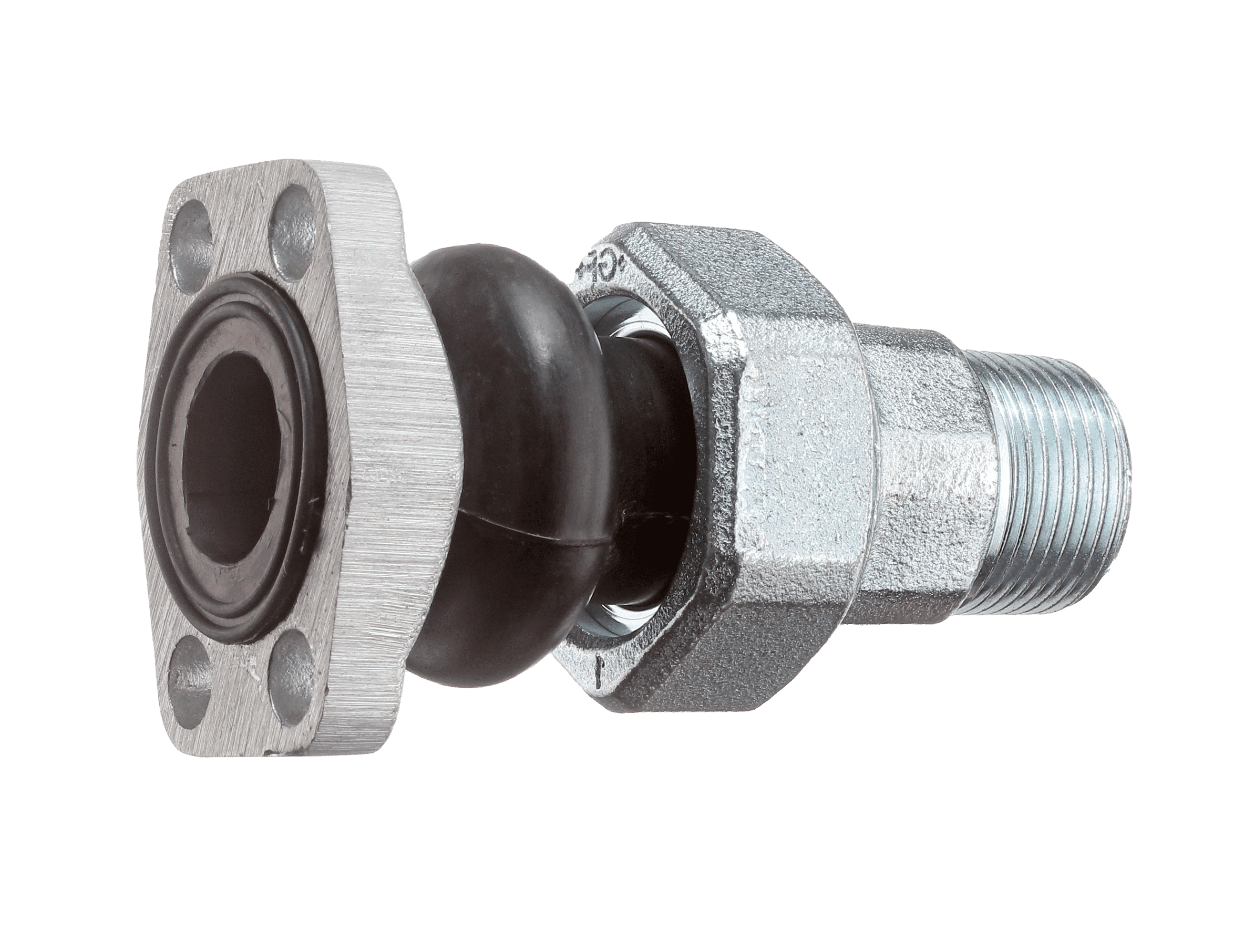
Compensator 101
What are rubber compensators?
Rubber compensators, also known as elastic expansion joints, protect piping by absorbing movement in axial and radial directions. They also compensate for slight offsets and misalignment caused by natural settling or installation imperfections. Their flexible design preserves seal integrity, prevents component damage, and reduces the risk of leaks at connection points—ultimately improving system efficiency and extending service life.
How are compensators used?
Rubber compensators are installed between the reservoir and pump. They are typically used in high-vibration systems to prevent vibration transfer to the rest of the components and system. They are also useful in high-maintenance applications where frequent pump removals can cause misalignment between the pipes.
Compensator Benefits
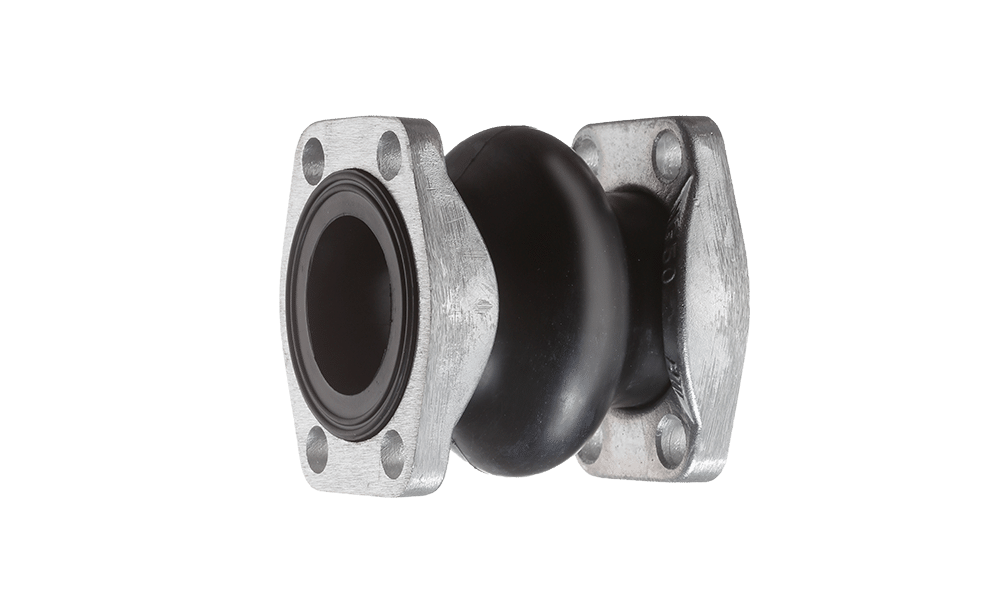

How to Choose a Compensator
Before selecting a compensator, ensure your system is compatible with the maximum operating pressure rating of up to 116 psi (8 bar) and no more vacuum than 10.2 psi (0.7 bar).
1. Select the correct size/nominal diameter
The compensator size corresponds to the pipe’s internal diameter. Hytorc offers diameters ranging from 1 to 4 inches (25 to 100 mm). For example, if the measured diameter is 1 inch, a 1-inch (25 mm) compensator would be the appropriate choice.
2. Choose required end connections
Compensators are designed for seamless integration into systems by using industry-standard flanges, such as SAE and DIN connections. The most popular mounting option is flanged threads, available in both aluminum and steel. Additionally, compensators can be equipped with threaded connections, made from steel.
3. Consider fluid compatability
Ensure correct fluid compatibility to prevent degradation. Hydraulic compensators typically use NBR (nitrile butadiene rubber) for the internal surface material.
Common acceptable fluids include:
• Water-glycol
• Water-soluble oil
• Kerosene
• Jet fuel
• Diesel fuel
• Gasoline
• Petroleum-based fluids
We offer a wide range of acceptable mediums. For questions on fluid compatibility, message us at us@icfluid.com.
Applications and Solutions
Compensators are essential in high-vibration systems and hard piping across industries like oil and gas, mining, marine, industrial manufacturing, construction, and transportation.
Construction and Mobile Equipment (Cranes, Trenchers, Drill Rigs)
All hydraulic systems, especially those in mobile applications, are subject to various movements and stress. Vibrations arise from regular operation of pumps and motors, while vibration from pressure and flow fluctuations can form due to varying changes of the load.
Mobile equipment, such as trench cutters, drill rigs, and cranes operate in rough terrains where the system itself faces constant jostling as it moves about its environment. This is why systems must employ some form of dampening component to protect the system.

