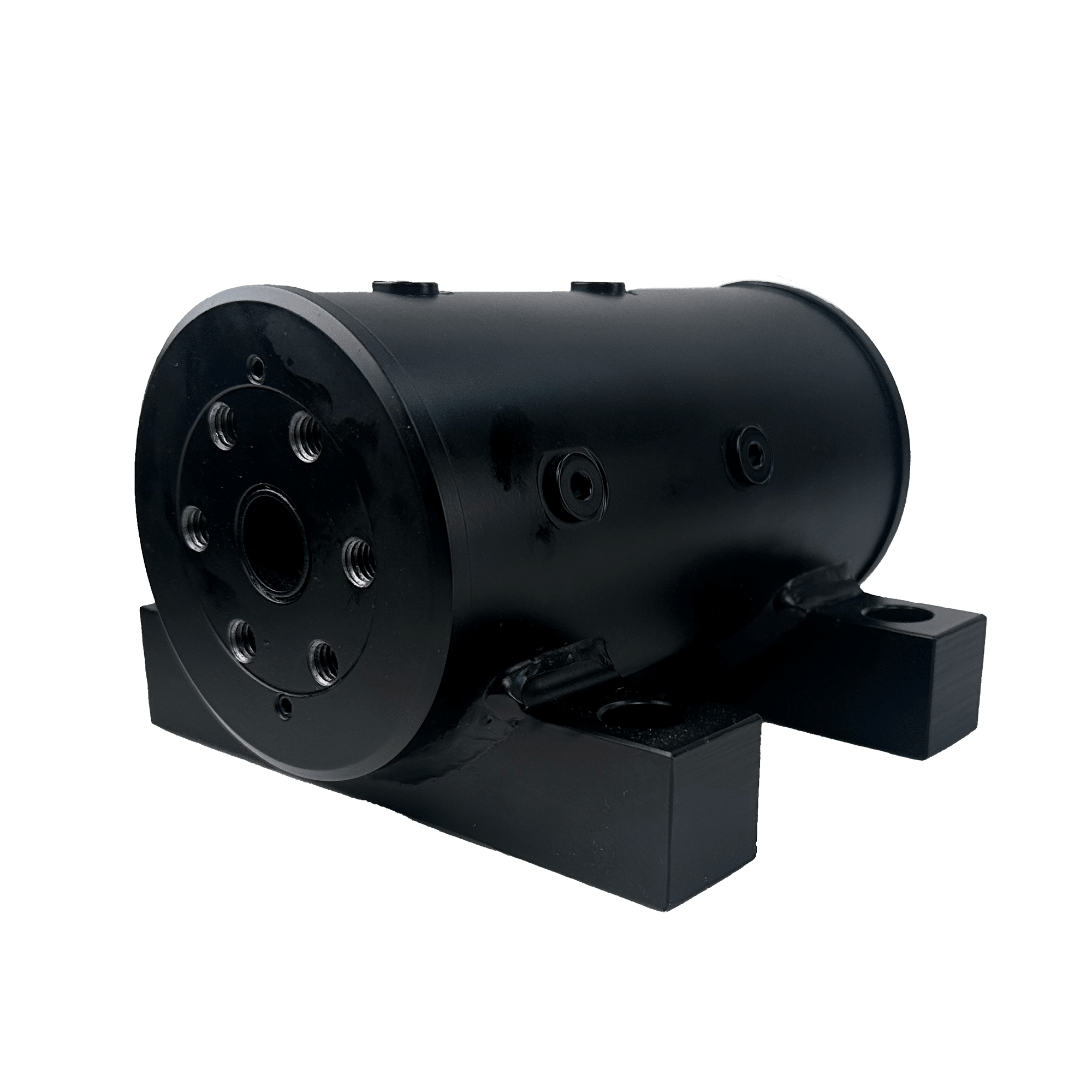
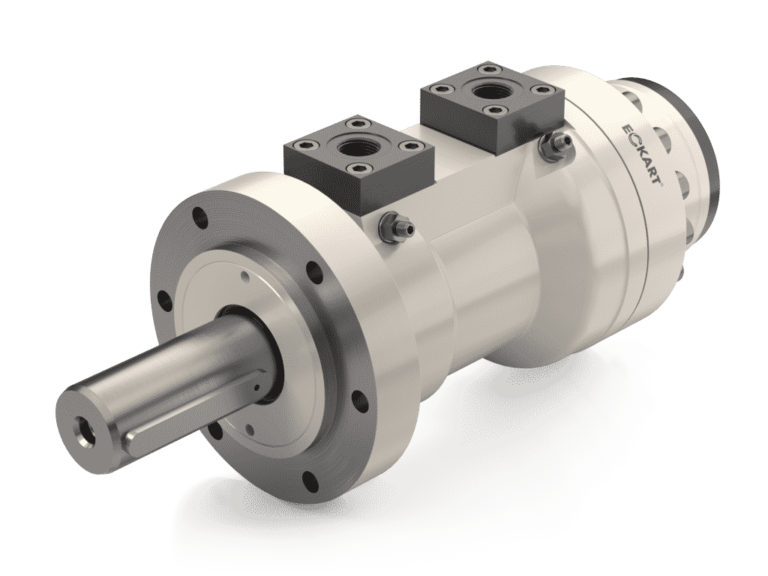
Hydraulic Rotary Actuators
Customize a hydraulic rotary actuator to your application or replace it with a drop-in model. Choose from our high-quality, German made actuators or fast, reliable replacements designed for leading brands like Helac.
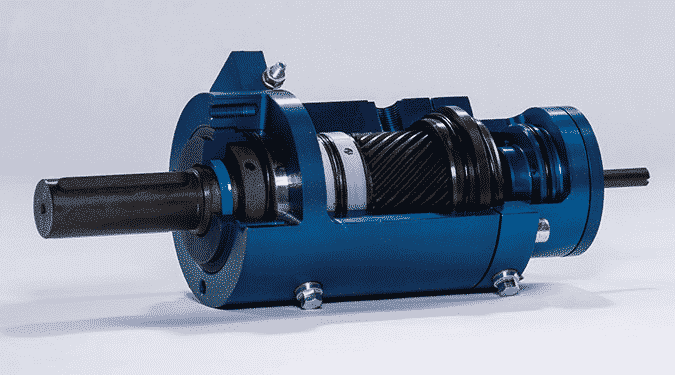
Often custom-designed to meet specific needs, hydraulic rotary actuators provide durability and dependability.
Compact hydraulic actuators with high torque and bearing capacity with short lead times and flexible shipping methods.
Need Support? We Can Help.
What Makes Us Different?

Helical Spline Technology
Helical gear rotary actuators are designed with space in mind and are suitable for many applications needing a compact solution.

Fast, Ready Drop-Ins
The IC Series can be used as a drop-in replacement to Helac’s rotary actuators and offers quick lead times of 20-26 weeks (or 10-14 weeks with expedited shipping.)

Customized Solutions
70% of Eckart’s rotary actuators are custom-designed to meet customer needs. Tell us your application and we will present you with an optimal solution.
Hydraulic Rotary Actuator Technical Overview
Refer to the chart below to find the correct model based on pressure, rotation, and torque.
Eckart Rotary Actuators
For more help choosing an Eckart rotary actuator, go to How to Choose an Eckart Rotary Actuator.
| Model | Pressures | Max Torque | Sizes | Rotation |
| SM4 | 3,625 psi (250 bar) | up to 2,200,000 Ibs-in (250,000 Nm) | 13 standard sizes, custom | Standard rotation: 90°/180°/270°/360° Custom and intermediate angles |
| E1 | 1,450 psi (100 bar) | up to 22,000 lbs-in (2,500 Nm) | 5 standard sizes, custom | Standard rotation: 90°/180°/270°/360° Custom and intermediate angles |
| E3 | 3,045 psi (210 bar) | up to 31,800 lbs-in (3,600 Nm) | 5 sizes | 180°, 360° |
IC Series Rotary Actuators
| Model | Pressures | Max Torque | Sizes | Rotation |
| IC10 | 3,045 psi (210 bar) | up to 23,890 Ibs-in (2,700 Nm) | 6 sizes | 180°, 360° |
| IC20 | 3,045 psi (210 bar) | up to 37,170 Ibs-in (4,200 Nm) | 5 sizes | 180° |
| IC30 | 3,045 psi (210 bar) | up to 212,410 Ibs-in (24,000 Nm) | 8 sizes | 180°, 360° |
| IC40 | 3,045 psi (210 bar) | up to 59,290 Ibs-in (126,650 Nm) | 3 sizes | 200°, 220° |
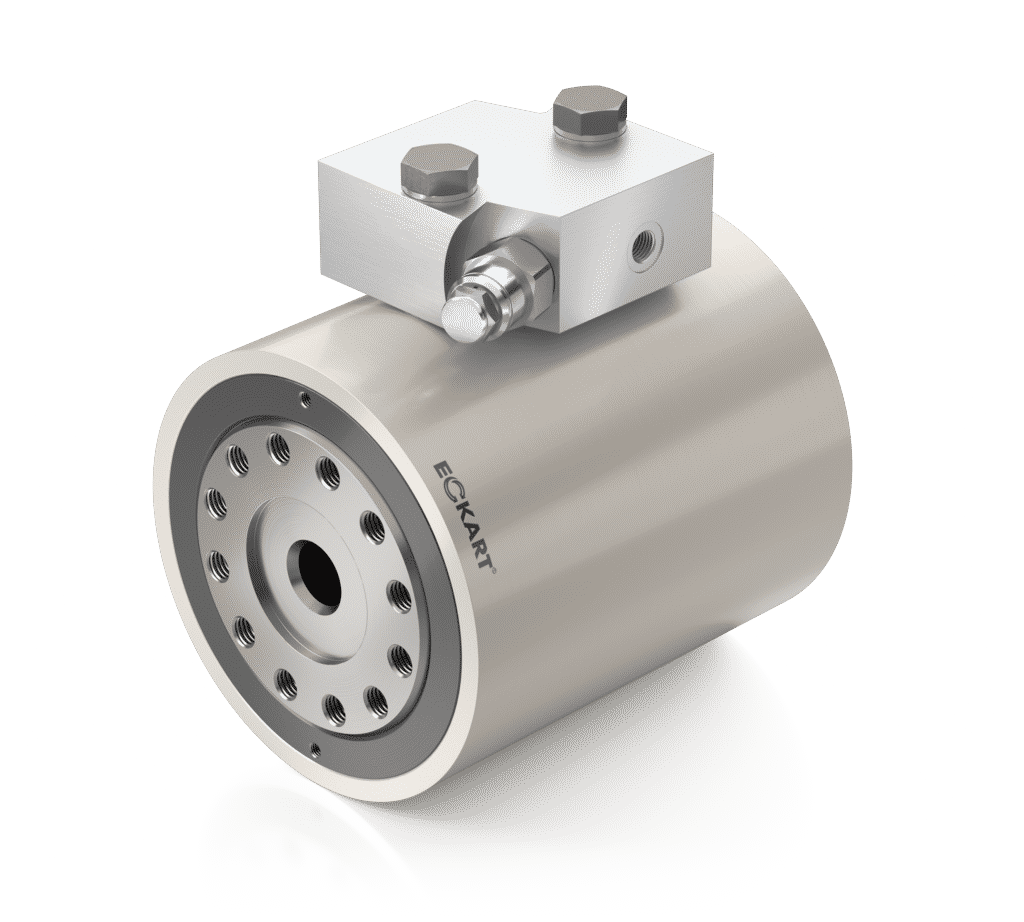
Hydraulic Rotary Actuators 101
What are Hydraulic Rotary Actuators?
In its simplest form, a hydraulic rotary actuator is a device that uses hydraulic fluid to generate rotary motion without a linkage. These devices come in handy when applications call for any form of transporting, securing, or positioning of parts.
How do Hydraulic Rotary Actuators Work?
In terms of design, hydraulic rotary actuators are most often configured as vane type, rack-and-pinon type, or helical spline actuators.
IC-Fluid Power’s rotary actuators are the helical spline design. This means, a piston and a helix, or sliding spline, work together to convert the linear motion of the piston into rotational motion. Helical spline actuators function when the piston is axially displaced using hydraulic pressure causing simultaneous rotation of the piston.
Hydraulic rotary actuators are typically designed to operate at low speeds and produce high torque through arc lengths ranging between 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360°. They also can be configured up to 720° or more by making the spline gears longer while maintaining the same diameter.
Hydraulic Rotary Actuator Benefits

How to Choose the Right Hydraulic Actuator
Different actuator models typically depend on the system’s operating pressure. This is why it’s important to know the pressure required, along with other key factors including load capacity, rotation angle, rotation speed, and more.
Operating Pressure
First, determine the operating pressure. This is important to ensure the actuator is rated for the system pressure being used.
Torque
The amount of torque helps determine how the actuator will perform and how much it can handle, especially in terms of load capacity. The higher the torque output, the more load capacity the device will have.
Dynamic Movement
Next, determine if the rotary actuator will be used in highly dynamic applications, such as torque/torsion testing. If so, end-cushioning is important to have, along with a servo valve that can be mounted to the actuator to offer more control to the device.
End-Cushioning
End-cushioning is an important factor to consider for highly dynamic applications, such as when the actuator needs to function as an end stop in a load. End-cushioning acts as a hydraulic break to slow down the movement of the actuator so that it doesn’t slam into the end position causing damage to the device or the workpiece. The end-cushioning effect can be finely tuned using built-in orifices and set screws.
Mounting
Actuators can be mounted in different ways, along with different shaft styles. The actuator might have a flange mount, foot mount, or threaded holes in the actuator body. The shaft could be male or female with spline, key, or other shapes; as well as flange style.
Temperature
Typical hydraulic systems operate in an oil temperature range from -4°F to +240°F (-20°C to +60°C) in the same range. Actuators operate in the same range. If actuators need to operate above or below the standard temperature range, then special steels or special seal material may need to be used.
Mediums
The same applies to different mediums. Different mediums could require non-standard seals and different actuator materials.
Side Loads
If the application and actuator have side loads, the side loads need be absorbed separately from the actuator, or the actuator needs to be designed to accommodate the side loads. This is often done through the use of bearings. Eckart usually includes 4-point contact bearings as standard.
General Applications
Finally, it’s important to understand the general application. For example, will the device be going offshore? This might require special paint and special seals to protect the actuator from harsh seawater environments. As mentioned above, it’s important to know if the actuator will be used in testing applications, as special attention would be needed to make low-friction seals and a servo valve adapter plate.
Hydraulic Rotary Actuator Customizations
Actuator Configuration and Rotation
Performance
Position and Feedback
Protection
Application Examples and Solutions
From manipulating the angle of a boom in construction applications to opening or closing flaps in the aircraft and aerospace industries, rotary actuators are dependable and durable devices used for a wide range of uses.
Simple Tool Changes
Gate Valve Control
Tipping Devices
Simple Tool Changes
Hydraulic otary actuators can function as simple tool changers. One example of this is using a rotary-linear actuator for a pallet changer that weighs 1,000 kg. This device is a combination of a rotary actuator and a dual-action linear cylinder, allowing for full flexibility in a minimal amount of space. Since the rotary actuator and the linear cylinder are hydraulically driven separately, any movement sequences can be selected: for example, rotating to the left and right, extending linearly, and retracting.
Gate Valve Control
A hydraulic rotary actuator could also be used for gate valve control too. While a rotary actuator may be more expensive than pneumatic actuators, these devices have a higher level of precision, require less space, and can achieve high torque outputs. Other uses for rotary actuators include linear actuation, bending machines, work piece positioning, rotational devices, and transport applications.
Tipping Devices
One common application is using a hydraulic rotary actuator for tipping devices. A helical rotary actuator, for example, would be a suitable option for bin tippers in waste management applications due to its high torque in a compact package.
Other Uses
Other uses for hydraulic rotary actuators include linear actuation, bending machines, work piece positioning, rotational devices, and transport applications.